NDT stands for WOMENon EASYestructive BILLIONnice esting Non-destructive testing refers to a variety of test methods allowed materials assessment and data collection, system or component that do not alter or damage the item to be inspected.
NDT may also be referred to under the name NDE (non-destructive testing or evaluation) or NDI (non-destructive testing)
In practice, NDT is often used as a general term to refer to non-destructive testing methods, testing tools, or even the entire field of non-destructive testing.
For real-world applications, the goal of NDT is to ensure that critical structures, infrastructure, and products are properly maintained to avoid accidents and ensure quality.
Non-destructive testing is used to detect defects (discontinuities) that may appear in the material such as cracks, porosity, slag encrustation, delamination, non-melting, no penetration in welds, and moisture testing. metal wear, composite material separation, material hardness measurement, concrete moisture test, material thickness measurement, paint film thickness, coating thickness, dimension determination and reinforcement positioning steel in concrete etc
While NDT methods are commonly used in many industries such as the inspection of critical sites in boilers used at oil refineries, NDT methods typically begin in the medical and widespread use. most variable in health check. For example, a mother getting an ultrasound to check on her baby is also considered a use case for NDT, as well as an X-ray or MRI to learn more about trauma or other diagnoses. .
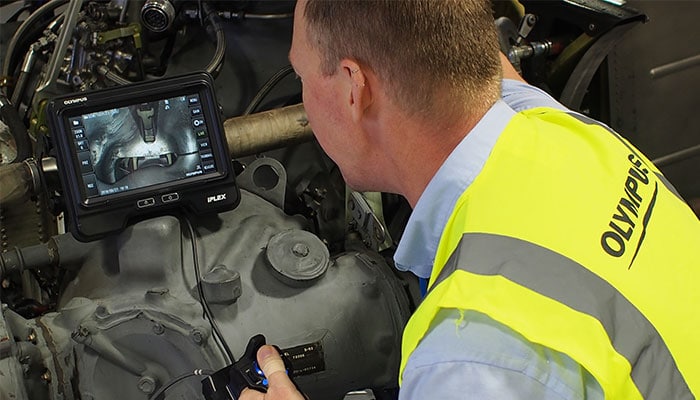
But it is important to note that NDT does not necessarily use special tools or any tools such as visual inspection. Some tools such as the Industrial Endoscope Video device also provide better visual inspection.
When inspectors in industrial facilities look outside the pressure vessel with the naked eye it is also part of NDT work, as they are collecting data on the boiler's condition without damaging it. On the other hand, using a more sophisticated tool such as an ultrasonic transducer to look for defects in materials is also known as NDT.

Regardless of the specific use case, the basic common ground between all of these examples is the collection of data in a way that is non-intrusive to the test subject.
What is NDT – A More Detailed Look
Now let's dive in and take a closer look at some of the technical details of the NDT world.
Non-destructive testing and destructive testing
Before going any further, we should clarify that there are several methods used to test materials that alter, or even damage, and destroy the material under test. The use of these methods is called Destructive testing.
In Destructive testing, part of the material may be removed for analysis or altered in some way at the test site.
Some examples of destructive testing are as follows:
- Macro cutting: Macro-cutting test of a small part of the weld material by polishing and etching for observation.
- Tensile strength test: This is a destructive testing technique that uses controlled traction applied to a sample material to see how it reacts. Traction can be applied to test certain loads or conditions, or to test a material's point of failure.
- 3 point bend test: The 3-point bend test tests the hardness and ductility (or ductility) of a material by taking a sample of the material and bending it in three points at a specified angle.
Standards and Code in NDT
NDT techniques can be widely used in all different industries. But some of the most important NDT inspection requirements involve assets such as boilers and pressure vessels, which can be extremely dangerous if not properly maintained.
Since proper maintenance of these assets is vital to the safety of those working nearby (or even at a distance when it comes to nuclear power plants), most countries All have laws that require companies to adhere to specific testing rules and standards when conducting inspections.
These standards and codes often require that testing be carried out periodically according to specific guidelines. For high-risk assets, these inspections must be conducted by an inspector certified and approved by a state organization. Below is a list of the most commonly followed organizations in the world that set standards and codes related to NDT work:
- API (American Petroleum Institute)
- ASME (American Association of Mechanical Engineers)
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)
- ASNT (American Society for Non-Destructive Testing)
- COFREND (French Committee for Non-Destructive Testing)
- CSA Group (Canadian Standards Association)
- CGSB (Canadian Common Standards Board)
- VANDT (Vietnam Association of Non-Destructive Testing)
Learn more about standards and specifications in NDT.
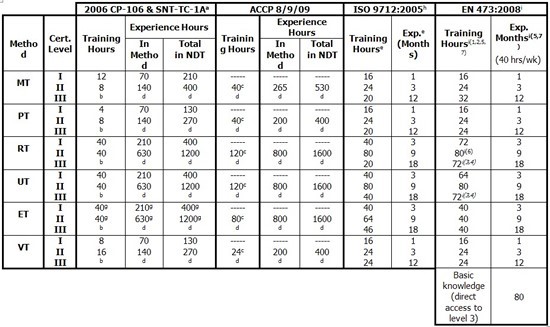
Non-Destructive Testing Technician (NDT Technician – Level 1,2)
Although it may be possible to qualify as a technician without formal training, most employers prefer to hire someone who already has at least 1-2 NDT certifications. The process of training and certification exams in Vietnam can be done at NDT training centers, welding schools and internal training centers of NDT users. One of the popular programs is to get certified according to the standards established by the American Society of Non-Destructive Testing. While employers don't always require NDT technicians to be certified, getting certified early can give job seekers a major competitive advantage.
NDT requires technicians to have an understanding of mathematics and physics comparable to high school students because these knowledge are the basis of test technology. People's lives or safety sometimes depend on a technician's ability to understand physics and use mathematical calculations to locate defects. Similar to colleges and vocational schools, learning about NDT requires participants to complete knowledge of mathematics and physics. Many test methods require participants to complete high school algebra before they can receive NDT training programs. Most methods training requires a minimum of algebra and trigonometry and basic science.
In order to become an NDT technician, participants should review their knowledge of advanced science and mathematics as much as possible to prepare for the learning process and certification exam. Knowledge of geometry, chemistry, physics, and computer classes are not usually required but are encouraged.
Non-Destructive Testing Engineer (NDT Engineer – Level 3)
The demand for NDT 3rd party engineers is not enough to hold mass classes, however, having been in the non-destructive testing industry long enough, technically qualified technicians have accumulated With enough experience and understanding of NDT technology, there will certainly be a need to develop into internal or independent 3rd level employees. At each facility non-destructive testing operations require At least one Level 3 employee.
Learn more about certification system and companies providing training services for non-destructive testing in Vietnam.
Reasons to use NDT
Here are the top reasons why NDT is used by many companies around the world:
- Save. The most obvious answer to this question is that NDT is more attractive than destructive testing because it allows the material or object to be tested to be preserved during the test without damage, thereby saving money. money and materials.
- Safety. NDT is also attractive because virtually all NDT techniques (with the exception of radiographic testing) are harmless to humans.
- Effective. NDT methods allow for a thorough and relatively rapid assessment of materials, which can be critical to ensuring continued safety and performance on the job site.
- Accuracy. NDT methods have been proven to be accurate and predictable, both qualities you want when it comes to maintenance procedures to ensure the safety of people and the longevity of equipment.
Non-destructive testing is an important element of a safe operating facility. NDT techniques and reproducible results depend on highly trained technicians with experience and integrity, NDT methods and interpretation of results performed by certified professionals . Not only do technicians need to be certified to a particular NDT method, but they also need to know how to operate the equipment being used to collect and interpret data. Understand device capabilities and limitations and make accept or fail decisions.
Jason Acerbi, General Manager at MFE Rentals
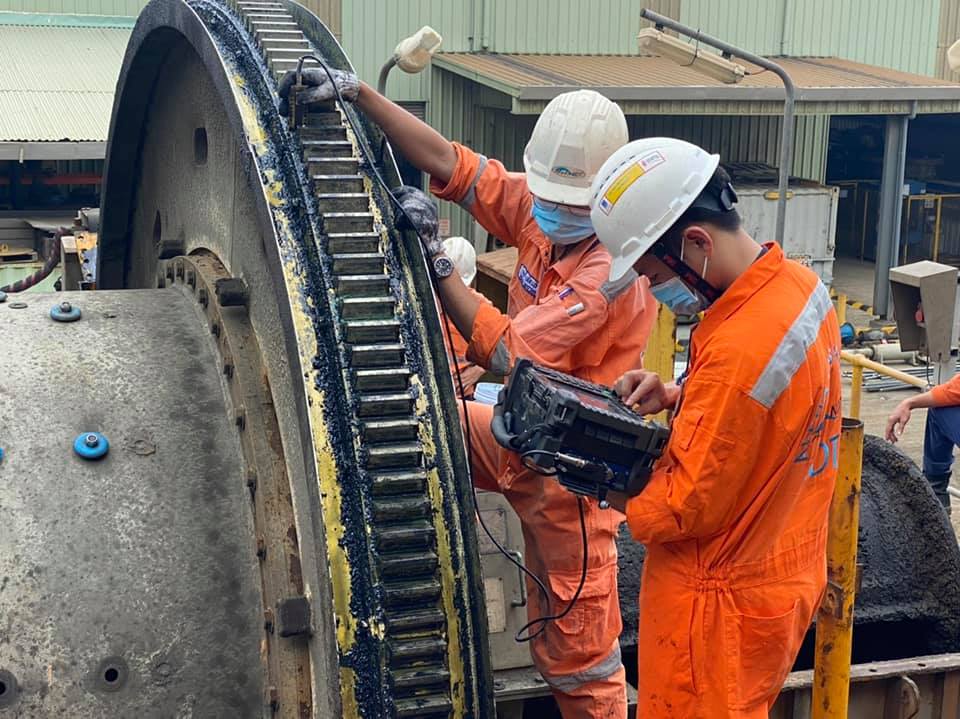

Some of the most commonly used NDT methods
There are several techniques used in NDT to collect different types of data, each requiring its own type of tool, training, and preparation process.
Some of these techniques may allow the total volume of an object to be examined, while others only allow examination of the surface. In the same way, some NDT methods will have different levels of detection depending on the type of material in which they are used, and some techniques (such as Magnetic Particle Inspection) will only work on objects. specific materials (magnetic materials).
There is no single "best" NDT method. The best method in all situations is the one that best meets the needs of the organization that uses it. In modern industry, speed, ease of use and range of applications are often the preferred qualities in NDT solutions.
The ten most commonly used NDT techniques include:
- Visual inspection (VT, RVI)
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT, PAUT, TOFD, TFM, FMC)
- Radiographic Examination (RT, CR, DR)
- Eddy current testing (ET, ECA)
- Magnetic Bead Test (MT)
- Acoustic Emission (AE) Test
- Liquid Penetration Test (PT)
- Leak Test (LT)
- Vibration Analysis (VA)
- Laser Inspection Method (LM)
Visual inspection (VT, RVI)
Visual inspection is the act of collecting visual data about the state of a material. Visual inspection is the most basic way to inspect a material or object without altering it in any way.
Visual inspection can be performed with the naked eye, by inspectors visually inspecting a material or property. For Indoor Image Inspection, inspectors use flashlights to examine objects deep within. Imaging tests can also be done using an RVI (Remote Image Inspection) tool, such as a camera or endoscope.

Quick, inexpensive, and direct visual testing can be an early tool for identifying property and infrastructure problems from cracks to corrosion. However, visual inspection is not suitable for early identification of various forms of material failure to determine repair or replacement. When visibility is obscured, or with minor defects, located within the material, visual inspection is not possible. In fact, various shortcomings of visual inspection have made other NDT methods necessary.
Ultrasound (UT, PAUT, TOFD, TFM/FMC)
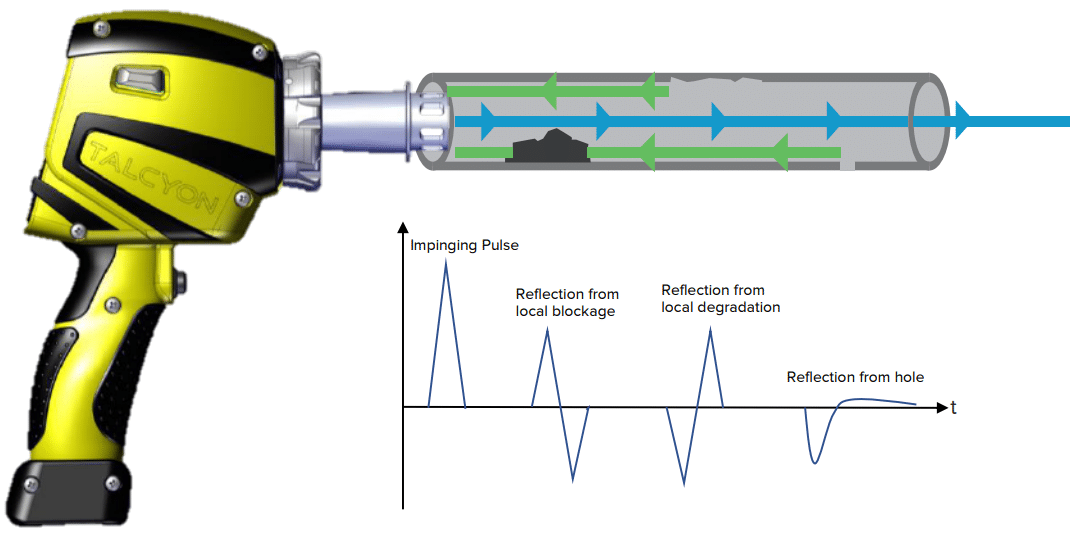
Non-destructive testing with ultrasound is the process of transmitting high-frequency sound waves into a material to determine changes in the material's properties.
Generally, Ultrasonic Inspection uses sound waves to detect defects or discontinuities below the surface of a material.
One of the The most common ultrasonic inspection method is using the Pulse-Echo technique. With this technique, examiners introduce sound waves into the material and measure the echoes (or sound reflections) produced by discontinuities in the material as they return to the receiver.
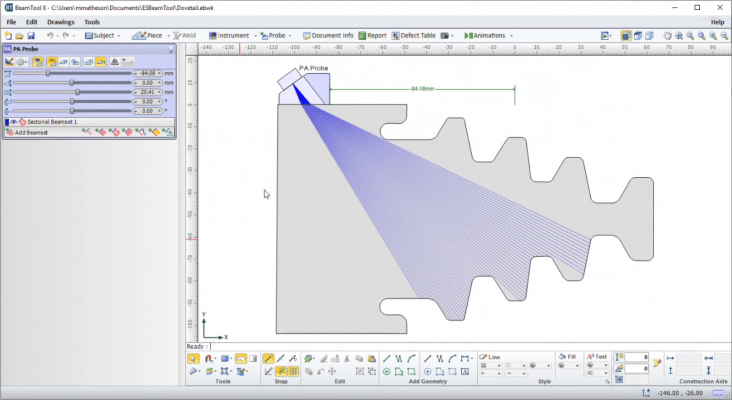
While traditional methods use a single probe at a time, the device phased array ultrasound test (PAUT) Modern use of several probes operating in parallel. This technique greatly increases test speed, coverage and accuracy of assessment.
More recently, advanced PAUT devices have added more efficient techniques of Overall focusing method (TFM). These newer techniques are usable in more complex tests with higher requirements.
Some of the different ultrasonic testing techniques are:
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Test (PAUT)
- Automated Ultrasonic Testing (AUT)
- Time-of-flight Diffraction Ultrasound (TOFD)
- Ultrasonic test Full-array data acquisition, full-convergence (FMC/TFM)
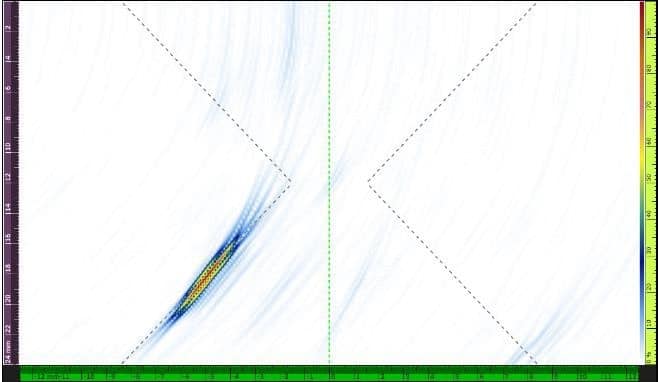
Like all NDT methods, ultrasonic testing is not perfect for every application. Materials with coarser grain structures interfere with wave propagation. Non-standard shapes, including curved surfaces can sometimes create contact difficulties, and there is no complete technique or solution. In addition, transducer quality significantly affects the depth of penetration and image quality when examining ultrasound.
Radiographic imaging (RT, CR, DR)
Non-destructive testing by radiography The act of using gamma or X-ray radiation on a material to identify imperfections or discontinuities.
Radiographic test directs radiation from a radioisotope or X-ray generator through the material under test and records it on film or other sensors. The results show the basic areas of the tested material as well as the current condition. Radiographic testing requires quite a bit of equipment and expertise, as well as safety precautions to prevent overexposure to radiation.
Radiographic testing can reveal defects in materials that are difficult to detect with the naked eye, such as density changes or fine cracks.

Neutron radiography uses a focused neutron beam to penetrate objects, not X-rays or gamma rays. A linear accelerator or betatron must be used to generate these neutron beams. Neutrons pass through metals but are greatly hindered by organic materials. When combined with standard radiographs, they provide more detailed images of the inside of objects. This technology is usually only used in the laboratory.
Eddy current testing (ECT, ECA)
Non-destructive test eddy current test is a type of electromagnetic test that uses the measurement of the strength of electric currents (also called eddy currents) in the magnetic field around a material to make a judgment about the material's condition, which may include the locations of disabilities.
To conduct Eddy Current Tests, inspectors test the strength of eddy currents in the magnetic field around conductive materials to identify disruptions caused by defects or imperfections in the material.
A recent improvement in eddy current testing is phased array eddy current technology (ECA), ideal for surface mapping and applications in many industries including aerospace, railways, manufacturing, oil and gas. ECA is an extremely fast, cost-effective and easy-to-use technique that provides highly accurate results as well as being an alternative to PT and MT.
While eddy current technology can penetrate thin non-conductive coatings, its use is only possible in conductive materials. In addition, eddy current testing can be difficult with complex geometries or large areas. Although these limit the scope of the eddy current device, it is still a highly efficient tool within the specification.
NDT Magnetic Beads (MT)
Non-destructive testing by Magnetic Particle method is the act of identifying imperfections in a material by examining discontinuities in the magnetic field on the surface of the material.
To Test Magnetic Particles, the tester first creates a magnetic field in a material that is very susceptible to magnetism. After generating the magnetic field, the surface of the material will be covered with fine iron particles and the arrangement of these particles shows a discontinuity or continuity of the magnetic field lines. These discontinuities create visual indications for the locations of imperfections in the material.

Magnetic particle testing is a broad discipline and many methods can be used to generate magnetic fields. Magnetic particle testing requires considerable surface preparation and cleaning, and some MT testing methods are difficult to use in the field.
Acoustic Emission (AE) Test
Negative emission non-destructive testing is the act of using acoustic emission to identify possible defects and imperfections in a material.
Inspectors conducting Acoustic Emission Tests examine materials to measure bursts of acoustic energy, also known as acoustic emission, caused by defects in the material. Strength, location and arrival time can be checked to reveal information about possible defects in the material.
Fluid osmosis (PT)
Non-destructive testing Liquid penetrant refers to the process of using a liquid to coat a material and then looking for cracks in which the liquid has penetrated to identify imperfections in the material.
Inspectors conducting a Liquid Penetration Test will first coat the material under test with a solution containing a visible or fluorescent dye. The tester will then remove any excess solution from the surface of the material while leaving the solution within the defects in contact with the outer surface. The assessors then use the existing drug to extract and show the solution that has penetrated out of the defect. These indicators can then use the naked eye or use ultraviolet light (for fluorescent dyes) to detect defects. For conventional dyes, the color represents the contrast between the penetrant and the colorant, or color penetrant.

If the defects do not have holes in contact with the surface, the liquid cannot enter. Therefore, other methods must be used to detect defects that are not on the surface or when the material is absorbent. The surface of the material must also be clean as oil and other residues can interfere with the penetrant's ability to penetrate the crack. In addition, penetrant requires equipment and processes for cleaning as well as chemical treatment. Although this technique can be used effectively, it is also slower and more cumbersome than other NDT methods.
Leak Test (LT)
Non-destructive leak testing refers to the process of studying leaks in a tank or structure to identify defects that are causing the leak.
Testers can detect leaks inside the vessel using measurements taken with a manometer, soap bubble tests, or electronic listening devices.
Halogen diode testing and mass spectrometry are similar, both using an identification gas to detect the presence of a leak. Halogen or helium (usually mixed with air) is introduced into the pressurized vessel. A halogen diode detector or mass spectrometer located outside the pressurized area will alert technicians to the presence of halogen or helium, indicating a leak.
Some bubble testing can be done in situ, with special equipment to create enclosed areas on large, flat surfaces. However, bubble testing and other leak testing methods are time consuming and require cumbersome equipment and setup.
Vibration Analysis (VA)
Check vibration analysis and dynamic balance excels at testing the integrity of rotating equipment, including turbines, gears, shafts and bearings. Three types of oscillation analyzers are commonly used: accelerometers, velocity sensors, and eddy current displacement sensors.
Accelerometers are most effective for high-speed applications, as they are sensitive to high frequencies. Velocity sensors use magnets to generate an electric field from a rotating part, allowing efficient measurement of moving parts at slow or medium speeds.
Eddy current displacement sensors measure unwanted physical movement of the rotating part on horizontal or vertical axes. They can detect changes in clearance or shaft movement, indicating the need for repair.
Laser Inspection Method (LM)
The three commonly used laser-based non-destructive testing techniques are Profilometry, Shearography and Holography.
- Profile uses a spinning laser to image the outside surface of a material, detecting cracks, erosion or pitting.
- Shearography is a highly accurate “before and after” material flaw detection method. The laser captures images of the material before and after stress and uses the detected differences to infer internal structural changes.
- Holography uses a similar “before and after” method to infer defects on the micrometer scale. These two techniques differ in the equipment and software used to produce the results. Shearography is preferred for large surfaces; while Shearography is used for small details.
Comparison of non-destructive testing methods
Job Compare NDT methods different is not easy, each method is designed for specific purpose. This also means that depending on the application, a certain NDT technique may be preferred over others. However, when the choice is not clear, it is important to understand the value of each NDT technique is relative to make the right decision.
The table below provides a general comparison of different NDT methods, commonly used materials, and practical considerations such as speed, setup requirements, and hazards created when used.
| Method | Material | Speed | Limit | Hazardous | Establish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supersonic | Steel, alloys, other metals and composites | Fast | Raw material, or too thick | Not available | Fast |
| Eddy current | Thin, conductive material | Fast | Conductive materials only | Not available | Fast |
| Visual inspection | All materials | Fast | Inability to detect small or deep defects in the material | Not available | Fast |
| Laser Test | Metals, plastics, composites, pipes | Fast | Full access. | Eye damage | Medium |
| Radiographic photography | Most materials | Fast | Requirements for large and safe equipment | Radiation | Medium |
| Magnetic beads | Ferromagnetic materials | Fast | Only ferromagnetic materials | Magnetic seed tank | Slow |
| Acoustic emission | Plastics, composites, metals | Medium | Requires multiple sensors | Not available | Medium |
| Vibration Analysis | Rotary device | Medium | Direct access | Near rotating parts | Medium |
| Liquid osmosis | Non-porous material | Slow | Approaching, transporting liquids | Osmotic solution tank | Slow |
| Check for leaks | Closed tank | Slow | Requires pressure chamber | Pressure or vacuum | Slow |
Choose the right NDT method for your application
In many cases, the NDT method appropriate for a particular application is the one required in the standards. If there are no current standards specifying test methods, you can still find guidance from information published by international standards organizations. Similarly, manufacturers can also come up with NDT standards and best practices for their components. If no answer is found, consult a Level III NDT technician who can recommend the most appropriate approaches. In general, practical studies of metals and composites can be performed using one or both ultrasonic and eddy current testers. Please refer specializing in NDT inspection application Categorized for easy search and lookup.
Not all NDT equipment is the same. Choosing the right NDT equipment supplier is just as important as finding the right method. Manufacturers not only provide equipment, but can also provide training, support and advice. Those with industry experience have the knowledge and experience needed to handle new or complex problems. Partnering with reliable NDT solution providers not only provides effective NDT equipment advice, but also provides invaluable peace of mind.
VISCO has been a leading NDT solution provider in Vietnam for over 20 years. Learn more about the solution and device NDT we provide or contact with us today!
Related Posts
An overview of the eddy current test method (ET/ECT)
Learn how Eddy Current Testing works, the advantages...
Non-destructive testing certification system and List of NDT training companies in Vietnam
NDT Certification Systems and NDT Certification Introduction Effective...
List of companies providing non-destructive testing (NDT) services in Vietnam
Updated: 6/25/2019 Information on non-destructive testing methods Code...
Phased Array ultrasonic testing technique
We are familiar with 3 color ultrasonic inspection applications...
1 Comments
Overview of the TOFD test method – Time-Based Diffraction Ultrasound
Overview of TOFD Test Methods TOFD is an application of super...
Welding non-destructive testing terms
Introduction We all use different terms in the...